The Louvre Museum in Paris houses one of the world’s most extensive and diverse collections of antiques. With over 380,000 objects and 35,000 on display, the museum showcases treasures from ancient civilizations including Egypt, Mesopotamia, Greece, and Rome. From iconic sculptures like the Venus de Milo to lesser-known but equally fascinating artifacts, the Louvre’s antique collection offers visitors a journey through thousands of years of human history and artistic achievement.
What Are the Most Famous Antiques in the Louvre Museum?

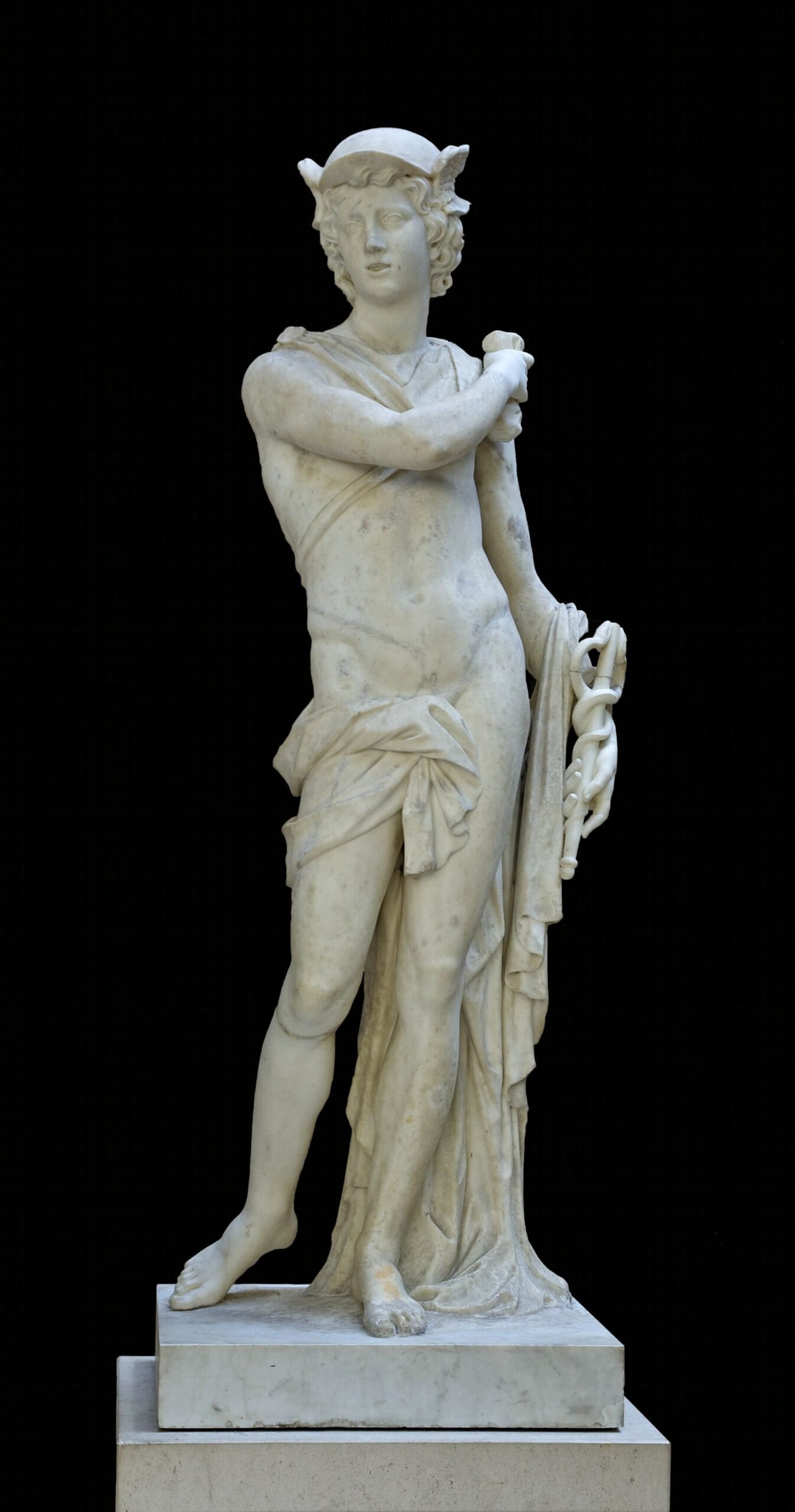
The Louvre Museum is home to some of the world’s most renowned antique artifacts. Here are some of the most iconic pieces:
- Venus de Milo: A marble statue of Aphrodite, discovered in 1820 on the Greek island of Milos.
- Winged Victory of Samothrace: A marble statue representing the goddess Nike, found in 1863.
- The Seated Scribe: A limestone sculpture from Ancient Egypt, known for its lifelike features.
- Code of Hammurabi: One of the oldest surviving legal codes, dating back to around 1754 BCE.
- The Great Sphinx of Tanis: A colossal sphinx that guards the entrance to the Egyptian Antiquities department.
How Extensive is the Louvre’s Antique Collection?
The Louvre’s antique collection is vast and diverse, covering multiple ancient civilizations:
- Greek and Roman Antiquities: Thousands of artifacts including sculptures, pottery, and jewelry.
- Near Eastern Antiquities: Over 100,000 objects spanning 9,000 years of history.
- Egyptian Antiquities: One of the world’s largest collections outside of Egypt, featuring mummies, sarcophagi, and monumental sculptures.
| Department | Number of Objects | Time Span |
|---|---|---|
| Greek and Roman | Thousands | 8th century BCE – 6th century CE |
| Near Eastern | 100,000+ | 9000 BCE – 7th century CE |
| Egyptian | 50,000+ | 4000 BCE – 4th century CE |
What Are Some Lesser-Known but Significant Antiques in the Louvre?
While the famous pieces attract the most attention, the Louvre houses many other significant antiques:
- The Human-headed Winged Bulls: Massive Assyrian sculptures over 13 feet tall.
- The Monzon Lion: A cast bronze lion from 12th or 13th century Spain.
- The gypsum statue from Ain Ghazal: One of the oldest works in the Louvre, dated to around 7000 BCE.
- The Sarcophagus of the Spouses: An Etruscan terracotta sarcophagus from the 6th century BCE.
- The Lady of Auxerre: A mysterious limestone statue from 7th century BCE Greece.
How Can Visitors Best Experience the Louvre’s Antique Collection?
To fully appreciate the Louvre’s antique treasures:
- Plan Ahead: The museum is vast, so prioritize which sections you want to see.
- Consider Guided Tours: Expert guides can provide context and highlight easily missed details.
- Use Audio Guides: Available in multiple languages, these offer in-depth information on key pieces.
- Visit During Off-Peak Hours: Early mornings or Wednesday and Friday evenings are often less crowded.
- Take Breaks: The collection is overwhelming; pace yourself and take time to reflect.
What Are the Practical Details for Visiting the Louvre’s Antique Galleries?
- Opening Hours: 9:00 AM to 6:00 PM (extended to 9:45 PM on Wednesdays and Fridays)
- Closed: Tuesdays, December 25, January 1
- Admission: Around €18 for a standard ticket, with various concessions available
- Accessibility: Wheelchair accessible with elevators and ramps
- Photography: Allowed without flash in most areas
How Does the Louvre Preserve and Study Its Antique Collection?
The Louvre employs state-of-the-art conservation techniques:
- Climate Control: Carefully monitored temperature and humidity levels
- Restoration Labs: On-site facilities for cleaning and repairing artifacts
- Research Partnerships: Collaborations with universities and other museums worldwide
- Digital Archives: High-resolution scans and 3D models for study and preservation
What Special Events or Exhibitions Focus on the Louvre’s Antiques?
The Louvre regularly hosts events centered around its antique collection:
- Temporary Exhibitions: In-depth looks at specific periods or themes in ancient art
- Lecture Series: Talks by curators and visiting scholars on various aspects of the collection
- Night Tours: Special after-hours tours focusing on specific galleries or themes
- Children’s Workshops: Educational programs introducing young visitors to ancient cultures
How Has the Louvre’s Antique Collection Influenced Modern Art and Culture?
The Louvre’s antiques have had a profound impact:
- Artistic Inspiration: Countless artists have studied and been inspired by these ancient works.
- Archaeological Understanding: The collection has been crucial in developing our knowledge of ancient civilizations.
- Cultural Diplomacy: The Louvre’s antiques play a role in international cultural exchanges and exhibitions.
- Popular Culture: Many pieces, like the Venus de Milo, have become iconic symbols recognized worldwide.
What Controversies Surround the Louvre’s Antique Collection?
Like many museums with extensive antique collections, the Louvre faces ongoing debates:
- Provenance Issues: Questions about the acquisition of certain artifacts during colonial periods
- Repatriation Requests: Some countries have called for the return of artifacts to their places of origin
- Conservation Challenges: Balancing preservation with public access and study
- Interpretation Debates: Ongoing scholarly discussions about the meaning and context of certain pieces
The Louvre Museum’s antique collection offers an unparalleled window into the ancient world. From monumental sculptures to intricate jewelry, these artifacts continue to captivate, educate, and inspire millions of visitors each year. Whether you’re a seasoned art historian or a first-time visitor, the Louvre’s antiques provide a rich and rewarding experience, connecting us to the artistic achievements and daily lives of our ancient ancestors.

